环境:
python3.5.2
涉及的库:
requests
bs4
pymysql
服务器:
Ubuntu16.04
1.代码
import requests
import datetime
import time
import pymysql
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import random
hottime=''#时间
sql = "insert into hottop(time,top)values(%s,%s)"
db = pymysql.connect("数据库的ip","数据库用户名","密码","weibohot")
cursor = db.cursor()
def Gethot():
url = 'https://s.weibo.com/top/summary?cate=realtimehot'
#这里为了稳定,可以添加一个user-Agent的池,然后每次用的时候随机一个,也可以添加ip池
header={
'User-Agent':'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64; rv:61.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/61.0'
}
try:
# global 声明接下来用的hottime是全局变量,
# 如果不加这个,它会变成局部变量,即使你在函数外声明了一个hottime
global hottime
hottime = datetime.datetime.now().strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S")
hotweb = requests.get(url, headers=header, timeout=10)
except:
print(hottime+':http Error')
else:
soup = BeautifulSoup(hotweb.text, "html.parser")
ans = soup.find_all('td')
top = ''
for i in ans:
a = i.find('a') # a标签内容,即热搜内容
span = i.find('span') # span标签内的的热度
if (a != None and span != None):
top += a.get_text() + '__' + span.get_text() + '\n'
return top
errorcount=0#5次错误跳出循环
while True:
try:
top = Gethot()
cursor.execute(sql,(hottime,top))
except Exception as e:
errorcount+=1
db.rollback()
print(hottime+":执行MySQL: %s 时出错:%s" % (sql, e))
if(errorcount==5):
break
else:
time.sleep(10)
continue
else:
db.commit()
time.sleep(random.randint(450,550))#每次sleep随机450-550秒2.数据表
| time | top |
|---|---|
| datetime | varchar(2000) |
DDL语句:(不设置utf-8可能会出错- -)
CREATE TABLE `hottop` (
`time` datetime NOT NULL,
`top` varchar(2000) NOT NULL
)DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;3.部署到服务器
如果你是在本地写的代码,先把文件上传到服务器(可以通过ftp啥的,方法多多),
关于运行,weibohot.py是代码文件, log.file是通过print输出的日志文件(可以不必先创建,运行下面命令它自己也会创建)
nohup python3 -u weibohot.py > log.file 2>&1 &nohup命令可以看这篇文章,我觉得介绍的很精简明要,现在市面上的云服务基本都给你装好了python2和3环境,直接用python命令的话一开始都应该默认为2,-u参数是不启用缓冲(否则你print出来的东西可能不会马上输出到log.file日志中)
其实仅仅如此还是不够的,它在运行中可能还会遇到各种问题之类的,因此想要更好的可以写个shell脚本,断线邮件提醒啊,重连啊…
4.结果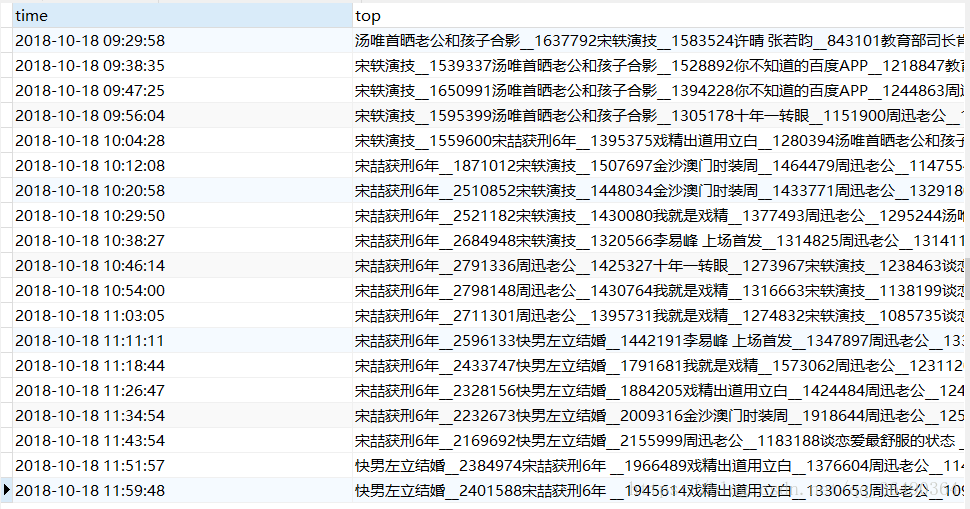
本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 CC BY-SA 3.0协议 。转载请注明出处!